Stem Cell Research
Our lab uses embryonic stem cells to investigate the effects of environmental chemicals on prenatal mammalian development. Human embryonic stem cells are currently the best in vitro model we have to study human development and how the environment affects cell survival, pluripotency, embryoid body formation, growth, and differentiation. We also have developed software to analyze dynamic behavior in pluripotent stem cell colonies, and we apply these software tools to live cell imaging data to mine information about cell behavior that cannot be extracted by human visualization (for more information see Video Bioinformatics).
We also use other stem and progenitor cell lines, such as mouse neural stem cells, human lung basal cells, and other in vitro models that incorporate multiple cell types.
Selected Publications
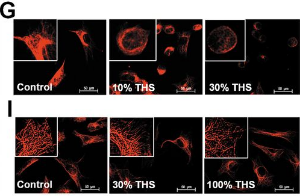
Cytotoxicity of Thirdhand Smoke and Identification of Acrolein as a Volatile Thirdhand Smoke Chemical That Inhibits Cell Proliferation.
Bahl V, Weng NJ, Schick SF, Sleiman M, Whitehead J, Ibarra A, Talbot P. Toxico Sci. 2016.
Thirdhand smoke (THS) is a mixture of chemicals that remain on indoor surfaces after smoking has ceased. These chemicals can be inhaled, ingested, or absorbed dermally, and thus could impact human health. We evaluated the cytotoxicity and mode of action of fresh and aged THS, the toxicity of volatile organic chemicals (VOCs) in THS, and the molecular targets of acrolein, a VOC in THS. Experiments were done using mouse neural stem cells (mNSC), human pulmonary fibroblasts (hPF), and lung A549 epithelial cells. THS-exposed cotton cloth was extracted in Dulbecco's Eagle Medium and caused cytotoxicity in the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. THS extracts induced blebbing, immotility, vacuolization, cell fragmentation, severing of microfilaments and depolymerization of microtubules in mNSC. Cytotoxicity was inversely related to headspace volume in the extraction container and was lost upon aging, suggesting that VOCs in THS were cytotoxic. Phenol, 2',5'-dimethyl furan and acrolein were identified as the most cytotoxic VOCs in THS, and in combination, their cytotoxicity increased. Acrolein inhibited proliferation of mNSC and hPF and altered expression of cell cycle regulatory genes. Twenty-four hours of treatment with acrolein decreased expression of transcription factor Dp-1, a factor needed for the G1 to S transition in the cell cycle. At 48 h, WEE1 expression increased, while ANACP1 expression decreased consistent with blocking entry into and completion of the M phase of the cell cycle. This study identified acrolein as a highly cytotoxic VOC in THS which killed cells at high doses and inhibited cell proliferation at low doses.